About
The SYMEXPO project aims to develop a “systemic approach to assessing the impact of urban mobility on exposure to environmental pollution,” based on a modeling framework in which a city dweller is represented as a mobile agent moving within a field of pollution subject to spatial and temporal variations. The environmental pollutants we take into account are noise and air pollutants.
To meet this challenge, an interdisciplinary team of internationally renowned experts in epidemiology, environmental acoustics, atmospheric pollutant dispersion, road traffic modeling, and environmental economics has been set up.
The project has led to advances in several key areas:
- Analysis of data from the MobiliSense cohort has shed new light on the mobility behaviors (modes of transport, activity patterns) most associated with high levels of noise exposure.
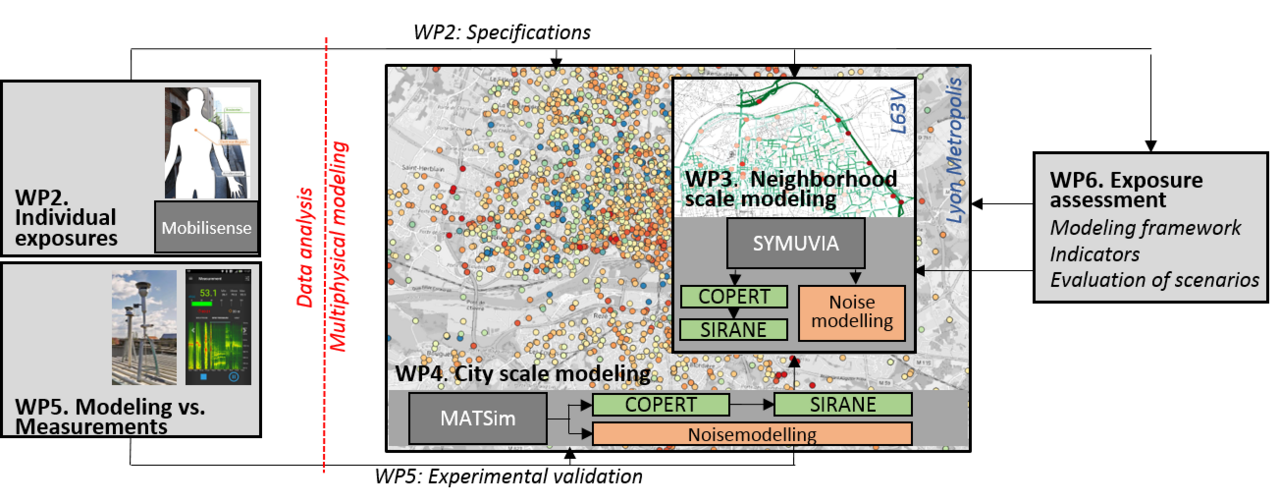
- Integrated open-source modeling chains were developed to simulate spatio-temporal variations in noise and air pollution at the neighborhood and metropolitan scales (see Figure 1). Two traffic models were used—SYMUVIA and MATSim—calibrated on the same study area in the Lyon metropolitan area. Noise modeling was based on the NoiseModeling platform, while air pollution modeling combined Copert/PHEM with the SIRANE dispersion model.
- The advantages and limitations of these dynamic modeling chains were analyzed. These new modeling chains were then applied to case studies focusing on exposure impact indicators, as well as to the assessment of socio-spatial inequalities, taking into account individual mobility. This made it possible to assess access to quiet areas or critical noise exposure areas.
More details on the results here